| Topics |
|---|
| Photometric residuals in g and r-bands |
| Discussion. |
Variations in photometric residuals between g and r-bands.
In order to understand how features in the spatial residuals, such as edge glints and dust spots, affect the photometry we compare the photometric residuals in g-band and r-band for the same CCD.
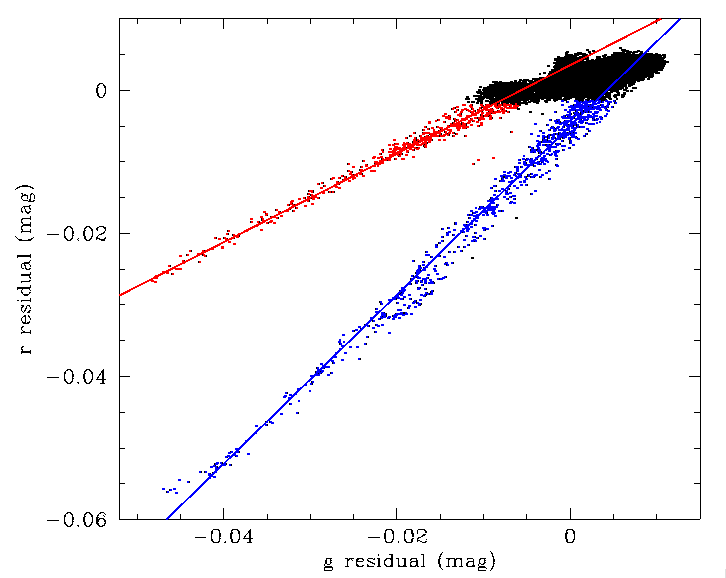
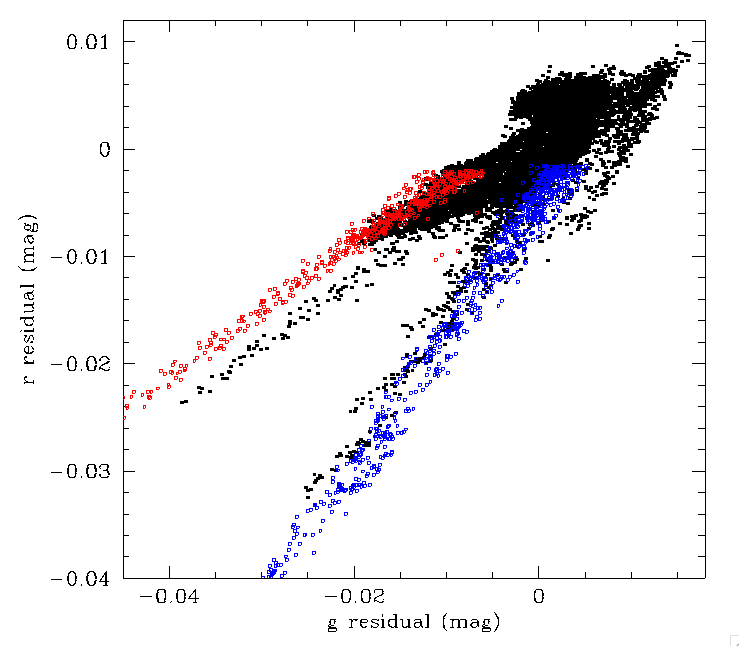
Photometric residuals in CCD6, quadrant 1 for ZTF g and r-band data. Here we see three general groups that have been plotted with different colours.
In plot above we show the relationship between photometric residuals in ZTF g-band and r-band for CCD-6, quadrant-1. We found three separate groups of related pixels. The black points relate to the underlying variation in colour response with CCD thickness, filter variations, etc. The blue points relate to edge-of-field glints. The red points relate to the dust spots. As we can see from the varying gradients, sources in these regions are expected to exhibit source colour relationships that vary from the overall CCD ones.
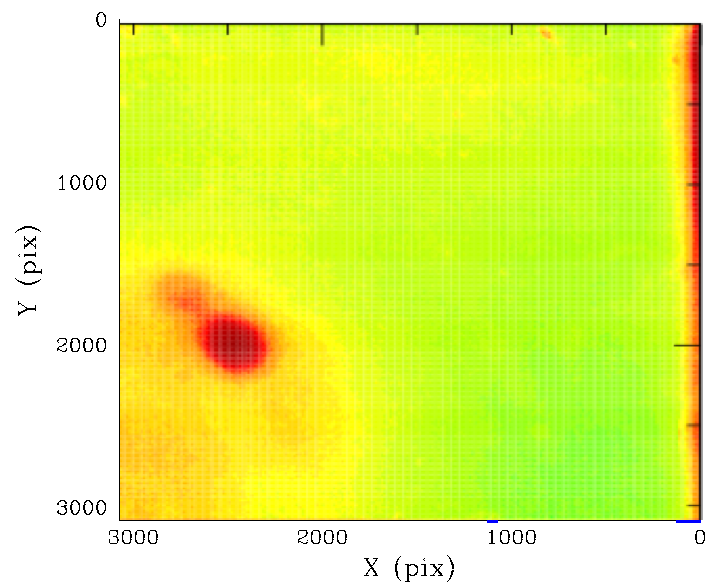
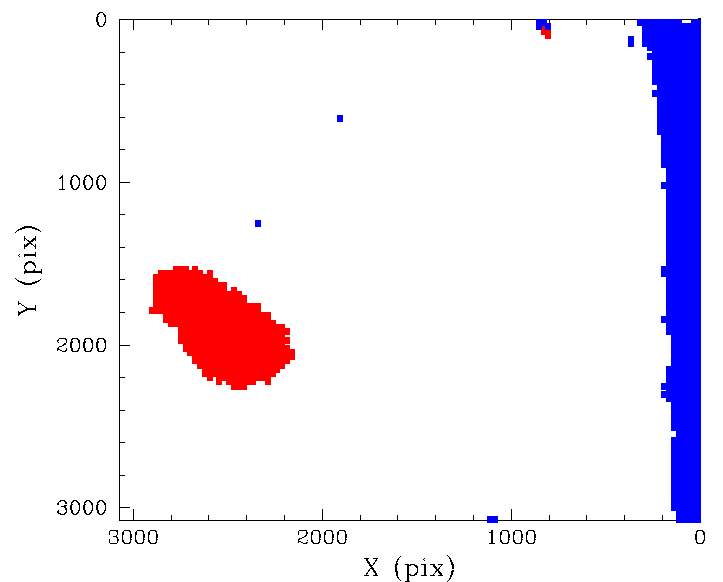
Photometric residuals maps and correspond location of pixels having a different colour response.
After removing the black points (the general photometric residuals), we plot the locations of the pixels corresponding to the red and blue point above. Clearly we see that the edge effects and dust spots have a different colour response in g and r. This agrees with the results of our prior analysis. Here we see that the edge glint effect (blue points) extends well into the CCD. The pixels affected by dust spots are also clearly well separated from reponse for the bulk of pixels.
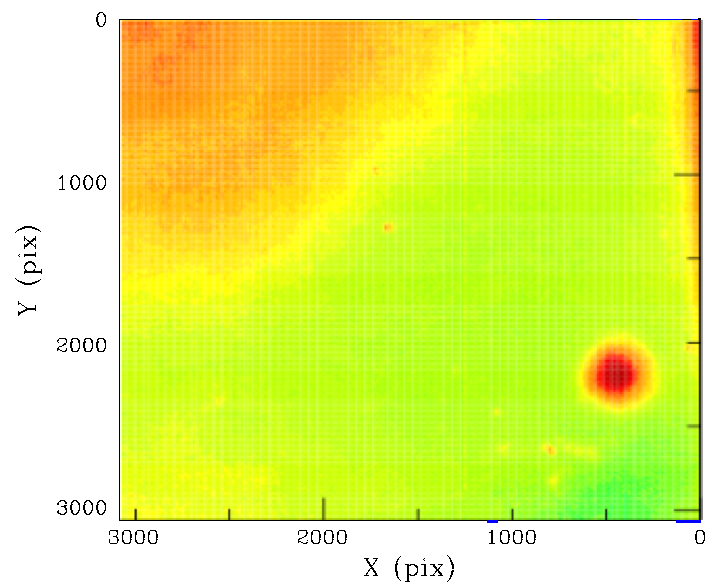
Spatial photometric residuals in CCD6, quadrant 4, g-band, and a comparison between ZTF g and r-band residuals in quadrants 1 and 4. The black points are the values for quadrant 4, while the blue and red points are the edge and dust spot pixel values for quadrant 1.
The spatial effects that we see in quadrant 1 are extreme examples of how dust spots and edge glints affecting the photometry. In the plot above we show the distribution of residual pixel values for quadrant 4 (which also has a large dust spot). Here we see that the residuals for edge glints and dust spots do not separate along the same lines as quadrant 1, and there is overlap between these points and pixels not affected by these features (due to offsets and scale differences between quadrants). This suggests that it may be necessary to select pixel regions with edge glints and dust spot by hand from multi-colour quadrant residuals. It may be possible to find all the dust spots as sources using SExtractor.
Since the number of pixels affected by edge glints and dust spots is a small fraction of a CCD, determining the colour response based on sources may be difficult. However, since the g vs r relationship for these sources is quite tight, there may be little variation in the colour effect within a spot or glint region.